The ultimate
Chrome extension tutorial
Thank you for the great book!"
Chrome extensions are everywhere.
- On average, 40% of internet users in the United States use an adblocker on any device; overwhelmingly, these adblockers take the form of browser extensions.
- The tech company Honey, whose primary product is a browser extension, was acquired by PayPal in 2020 for $4 billion.
- There are roughly 2 million apps in Apple's App Store; The Chrome Web Store has over 200,000 extensions.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1: What Are Browser Extensions?
01Meet the modern web’s most powerful add‑ons. This chapter traces how extensions evolved from early plug-ins to today’s secure, sandboxed marvels, and why they matter to builders, businesses, and power users alike.
- History of Browser Extensions
- Customizing Software with Plug-ins
- History of Web Browsers
- Native Browser Plug-ins
- Origins of Browser Customization
- Emergence of Modern Extensions
- The Browser Extension Landscape
- Comparing Mobile Apps and Browser Extensions
- Browser Extension Marketplaces
- Types of Browser Extensions
Chapter 2: Fundamental Elements of Browser Extensions
02Learn the core moving parts: where code runs, how pages, tabs, and origins interact, and which extension surfaces users will actually touch.
- The Browser Model
- Browser Tabs
- Same-Origin Policy
- The Browser Extension Model
- Independent JavaScript Pages and Runtimes
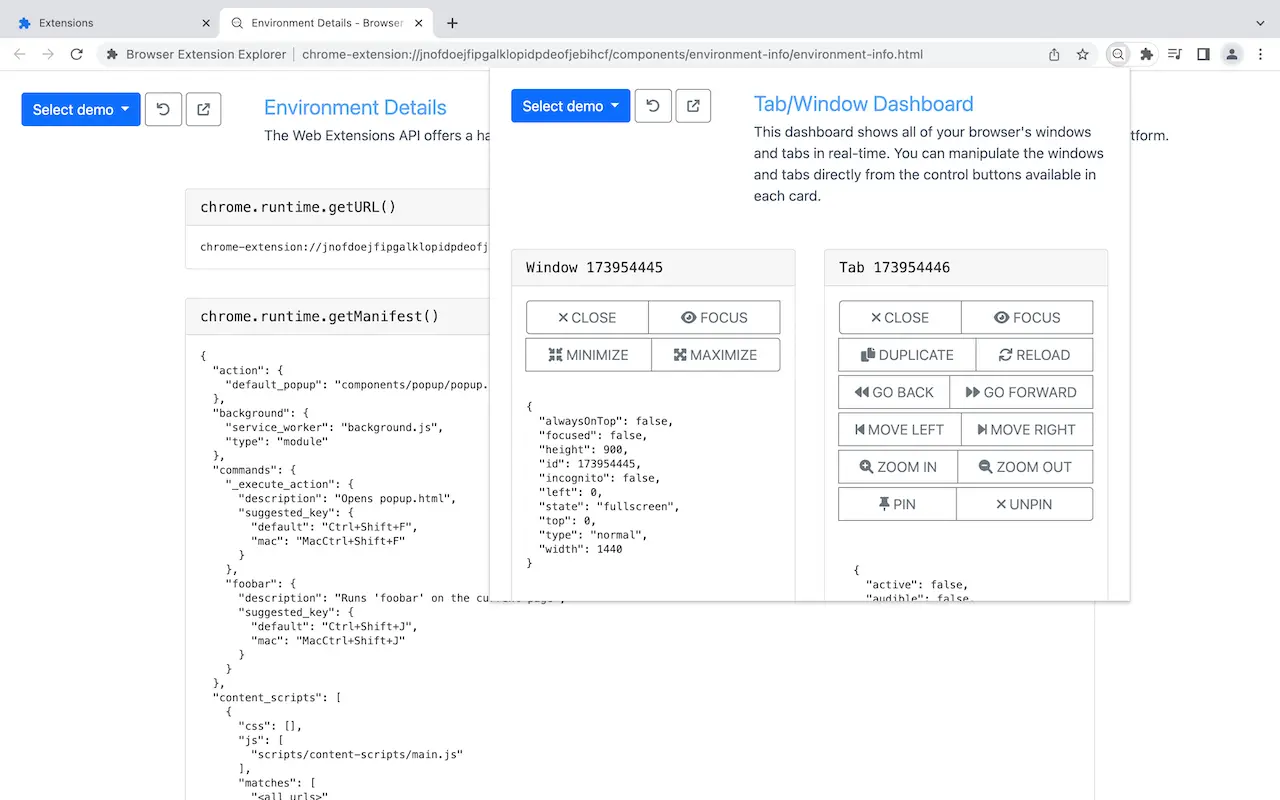
- Native APIs and User Interfaces
- Tab and Domain Access
- Observing and Intercepting Network Requests
- Elements of Browser Extensions
- Extension Manifest
- Background Scripts
- Extension UI Pages
- The Popup Page
- The Options Page
- The Side Panel
- Content Scripts
- Devtools Panels and Sidebars
- Extension Elements in Action
- Bitwarden
- Grammarly
- React Developer Tools
- Sider.ai
Chapter 3: Browser Extension Crash Course
03Spin up a minimum viable extension, install it locally, wire up the core files, and see the end‑to‑end workflow in action.
- Creating the Manifest
- Minimum Viable Extension
- Installing Your Extension
- Reloading Your Extension
- Building the Extension Skeleton
- Adding a Background Script
- Adding a Popup Page
- Adding an Options Page
- Adding a Side Panel
- Adding a Content Script
- Tying Everything Together
- Programmatically Opening Options and Side Panel
- Adding a Welcome Message
- Triggering a Content Script Render
Chapter 4: Browser Extension Architecture
04Understand lifecycles, file serving, content isolation, and how all the pieces coordinate reliably across updates.
- Architecture Overview
- Plurality, Lifecycles, and Updates
- Background Service Worker
- Extension UIs
- Devtools Pages
- Content Scripts
- Browser Extension File Server
- Sandboxed Pages
Chapter 5: The Extension Manifest
05Master the manifest fields that define capabilities, UI, permissions, and cross‑browser behavior.
- The Manifest File
- Supporting Different Locales
- Match Patterns and Globs
- Manifest Version
- Manifest Properties
- action
- author
- automation
- background
- browser_action
- browser_specific_settings
- chrome_settings_overrides
- chrome_url_overrides
- commands
- content_capabilities
- content_scripts
- content_security_policy
- converted_from_user_script
- cross_origin_embedder_policy
- cross_origin_opener_policy
- declarative_net_request
- default_locale
- description
- developer
- devtools_page
- differential_fingerprint
- event_rules
- externally_connectable
- export
- file_browser_handlers
- file_system_provider_capabilities
- homepage_url
- host_permissions
- icons
- import
- incognito
- key
- manifest_version
- minimum_chrome_version
- nacl_modules
- name
- oauth2
- offline_enabled
- omnibox
- optional_host_permissions
- optional_permissions
- options_page
- options_ui
- page_action
- permissions
- platforms
- replacement_web_app
- requirements
- sandbox
- short_name
- side_panel
- storage
- system_indicator
- tts_engine
- update_url
- version
- version_name
- web_accessible_resources
Chapter 6: Background Scripts
06Write robust background service workers, handle events predictably, and keep logic resilient.
- Web Page Service Workers vs. Extension Service Workers
- Service Worker Similarities
- Service Worker Differences
- Manifest V2 vs. Manifest V3
- Scripts vs. Service Workers
- JavaScript Imports
- No Access to DOM and Limited Global APIs
- Nonpersistent
- No Shutdown Event
- No Programmatic Background Access
- Working with Background Scripts
- Inspecting Background Service Workers
- Service Worker Errors
- Service Worker Termination
- Common Patterns
- Event Handler
- Secret Management and Authentication
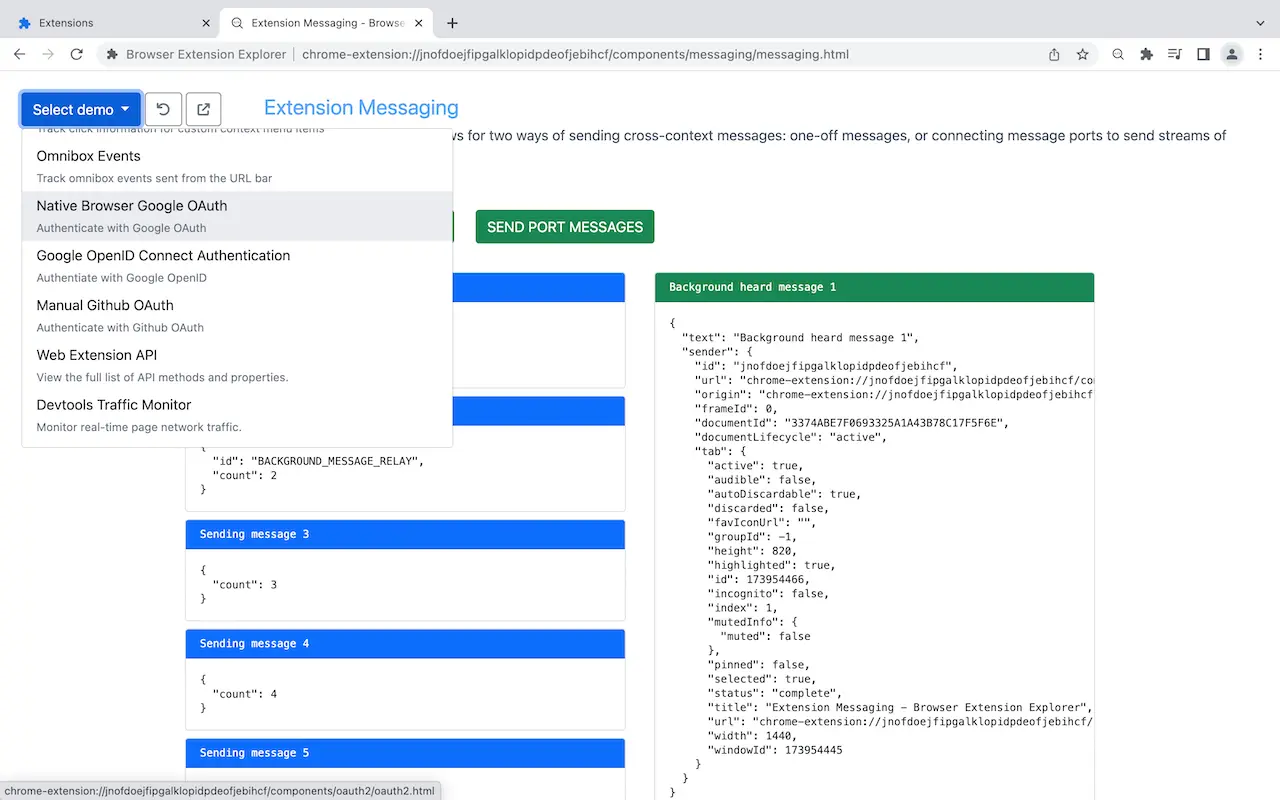
- Message Hub
- Storage Manager
- Injecting Scripts
- Sniffing Web Traffic
- Installed/Updated Events
- Opening Tabs
- Forcing Service Worker Persistence
Chapter 7: Extension UIs
07Design fast, focused UIs for popups, options, side panels, and DevTools that feel native and convert users.
- Introduction to Extension UIs
- Managed Pages
- Popup UI
- Options UI
- Side Panel UI
- DevTools UI
- Detecting Extension UI State
Chapter 8: Content Scripts
08Inject scripts and styles safely, communicate across worlds, and automate pages without breaking (or being broken by) them.
- Introduction to Content Scripts
- WebExtensions API Access
- Injected JavaScript and CSS Behavior
- CSS Injection Specificity
- JavaScript Injection Context
- Static Asset URLs
- Specialized Content Script Properties
- Injection Timing
- Script Worlds
- Matching Rules
- Stale Content Scripts
- Spoofed Network Requests
- Logging and Errors
- Page Automation
- CSS Isolation
- Modules and Code Splitting
- Bundling
- Dynamic Imports
- Dynamic Script Tags
- Programmatic Injection
- Injecting Inline Functions or Styles
- Passing Arguments
- Injecting Files
- Registration/Unregistration
Chapter 9: Extension and Browser APIs
09A practical, cross‑browser reference to the APIs that unlock storage, messaging, tabs, networking, AI, and more.
- Standards and the Role of W3C
- Global API Namespace
- Promises vs. Callbacks
- Error Handling
- Context-Restricted APIs
- Events API
- Format
- Event Filtering
- WebExtensions API Quick Reference
- Permissions
- Messaging
- Storage
- Authentication
- Network Requests
- Internationalization
- AI
- Browser and System Control
- Page and Screen Capture
- Proxy
- Browser State Management
- Tabs and Windows
- User Scripts
- Debugger
- Search
- Alarms
- Scripting
- DOM
- Offscreen
- Text to Speech
- Privacy
- Idle
- DevTools
- Extension Introspection
- Extension Management
- System State
- Enterprise Only
- Firefox Only
- ChromeOS Only
- Deprecated
Chapter 10: Permissions
10Learn strategies for permission prompts, optional grants, warnings, and review‑friendly scopes that won’t tank installs.
- Permissions Basics
- Checking Permissions
- Using Optional Permissions
- Granting Permissions Declaratively vs. Imperatively
- Permission Request Idempotence
- Shared Permission Grants
- Host Permissions
- Permissions Lifetime
- Permissions Warnings
- Testing Permissions Warnings
- Considerations for Published Extensions
- Triggering the Slow Review Queue
- Auto-disable Updates
- Permissions List
Chapter 11: Networking and Authentication
11Architect reliable auth, handle cookies and tokens, implement OAuth/OpenID, and choose the right network interception model.
- Comparing Websites and Extensions
- Networking Architecture
- Extension UIs
- Content Scripts
- Background Scripts
- Pinning an Extension ID
- Authentication Styles
- No Authentication
- Spoofed Authentication
- Cookie Authentication
- JSON Web Token Authentication
- OAuth and OpenID
- OAuth, OpenID, and the Identity API
- OAuth API Methods
- OAuth Redirect URLs
- Configuring the Authorization Platform
- Additional Help
- OAuth and OpenID Examples
- Google OAuth with getAuthToken()
- Google OpenID with launchWebAuthFlow()
- Auth0 PKCE Authentication
- Extension Authentication with Firebase
- Networking APIs
- The webNavigation API
- The webRequest API
- The declarativeNetRequest API
Chapter 12: Extension Tutorials
12Learn by building. Ten guided projects, from notepad to monetized products, cover real‑world patterns, testing, and polished UX.
- Notepad
- Tab Manager
- Screenshot Capture
- Screenshot Viewer
- Password Manager
- Ad Blocker
- LLM Chatbot
- On-device AI Summarizer
- User Scripts
- DevTools
- Monetized Extension
Chapter 13: Developing, Publishing, and Managing Extensions
13Instrument, test, publish, update, and manage at scale without sacrificing stability or user trust.
- Local Development
- Inspecting Your Extension
- File Changes
- Error Monitoring
- Extension Reloads
- Automated Extension Tests
- Unit Tests
- Integration Tests
- Additional Reading
- Publishing Extensions
- Store Listing
- Privacy Practices
- Review Process
- Beta Testing with Trusted Testers
- Updating Extensions
- Update Considerations
- Cancelling Updates
- Automated Rollback
- Automated Publishing
- Tracking User Activity
- Dashboard Metrics
- Analytics Libraries
- Install and Uninstall Events
- Enterprise Extension Management
- Enterprise Web Store
- Force-Installing or Blocking Extensions with Enterprise Policies
Chapter 14: Cross-Browser Extensions
14Navigate marketplace quirks, API gaps, and Apple/Safari specifics to maximize reach without multiplying code.
- Introduction to Cross-Browser Support
- Browser Coverage Tradeoffs
- Browser Share
- Chromium Browser Extension Sharing
- Adapting Your Code Base
- API Probing
- Differential Manifests
- Extension Marketplaces
- Marketplace Similarities
- Marketplace Differences
- Chrome Web Store
- Add-ons for Firefox
- Microsoft Edge Add-ons
- Safari Extensions App Store
- Opera Addons
- Mobile Extensions
- Mobile Extension User Interfaces
- Mobile Chrome Extensions
- Firefox Mobile
- iOS Safari
- Automated Deployment
- WebExtensions API Support
- Safari Extension Development
- Prerequisites
- Architecture
- Creating an Extension Project
- Writing the App
- Testing on macOS
- Testing on iOS
- Deploying to the App Store
- Converting an Existing Extension
- Firefox Idiosyncrasies
- Manifest Versions
- Sidebars
- API Additions
Chapter 15: Tooling and Frameworks
15Use React, HMR, and purpose‑built frameworks like WXT or Plasmo to ship faster with less boilerplate.
- Building Extensions with React
- Reactive State Management
- Routing
- Mozilla Tools
- web-ext
- webextension-polyfill
- Hot Module Replacement (HMR)
- Bundlers
- Vite
- Parcel
- Webpack
- Frameworks
- WXT
- Plasmo
- Extension.js
- Useful Sites